# install.packages("here")
library(here)Summaries and visualization of distributions
Reflection on the last week
Objectives
At the end of the lecture, you will know how to..
- Organize your code in scripts.
- Organize your work in projects.
- Count and interpret descriptive statics characterizing central tendency of a numeric variable.
- Describe spread of a numeric variable.
- Read plots for one variable.
- Create plots displaying one variable in
ggplot2package. - Understand what type of variation occurs within your variables.
Organize your work in scripts
dartpoints.r
# Analysis of dartpoints data set
# 6. 3. 2024
library(ggplot2)
# data -------------------------------
# read data from CSV
# url: https://petrpajdla.github.io/stat4arch/lect/w02/data/dartpoints.csv
dartpoints <- read.csv("dartpoints2.csv")
# structure --------------------------
colnames(dartpoints)
nrow(dartpoints)
ncol(dartpoints)
str(dartpoints)
mean(dartpoints$Length)
# plots ------------------------------
ggplot(data = dartpoints) +
aes(x = Length) +
geom_histogram() +
labs(x = "Length (cm)", y = "Count")
In RStudio…
- Create a new script with Ctrl + Shift + n
- Put some basic info on what are you doing at the top.
Use comments#(Ctrl + Shift + c) to write notes.
Comment on the why, not the what. - Divide the code into sections with Ctrl + Shift + r
# Section name ---- - Load the packages you use at the top of the script.
- RStudio will give you hints, hit Tab to autocomplete function calls.
- Execute the current line with Ctr + Enter
- Source the whole script with Ctrl + Shift + Enter
Organize your work in projects
- Each project is in a separate directory.
- There are subdirectories for different parts of the project.
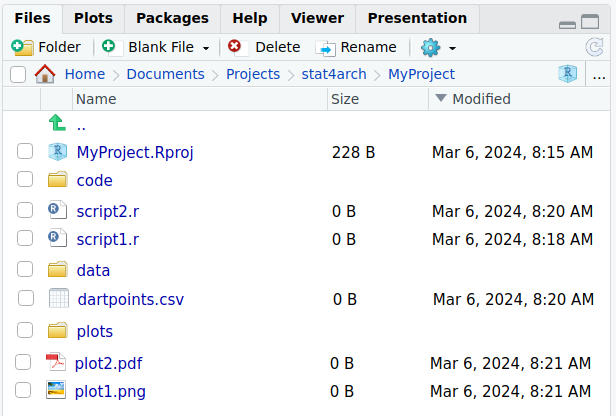
MyProject/
code/
script1.R
script2.R
data/
dartpoints.csv
plots/
plot1.png
plot2.pdf
MyProject.Rproj- In RStudio go to Files > New Project
Paths
Absolute file path
The file path is specific to a given user.
C:/Documents/MyProject/data/dartpoints.csvRelative file path
If I am currently in MyProject/ folder:
./data/dartpoints.csvPackage here is here to save the day!
- Do not forget to install the package first.
- Load it at the top of your script.
- Function
here()will know where the top directory is.
# read data ----
dartpoints <- read_csv(here("data/dartpoints.csv"))Descriptive Statistics
Characterizing centrality
Mean (průměr)
mean(x)
\[ \overline{x} = \frac{x_1 + x_2 + \cdots + x_n}{n} = \frac{1}{n} (\sum^n_{i=1}x_i) \]
Median (medián)
median(x)
- Robust, minimizes influence of outliers.
What are outliers? (odlehlé hodnoty)
- Outliers are data points that significantly differ from other observations.
- May indicate a measurement error, an exceptional observation, etc.
Characterizing centrality
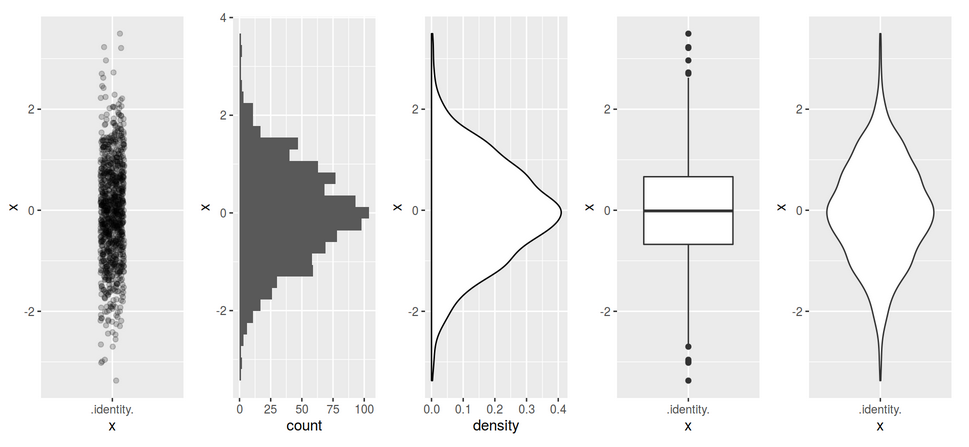
Characterizing dispersion and/or spread
Range (rozpětí)
max(x) - min(x) or range(x)
Variance and Standard deviation (rozptyl a směrodatná odchylka)
sd(x)
\[ \sigma = \sqrt{s^2} = \sqrt{\frac{\sum(x_i-\overline{x})^2}{n-1}} \]
Interquartile range (midspread, IQR, kvantil, mezikvartilové rozpětí)
IQR(x)
- Robust, minimizes influence of outliers.
Characterizing dispersion and/or spread

Exercise
- Start RStudio.
- Create a new project, save it somewhere you can find it.
- Use dataset dartpoints2.csv.
- Save it in your project directory.
- Load the data from the CSV file.
- What is the column separator?
- How are NAs represented?
- Explore the dataset.
- Count mean and median weight, how do they differ?
- What is the range of the weights?
- What is the standard deviation of weights? What does it mean?
- Count the IQR. Compare it with standard deviation.
- Hints:
read.csv2(path, na.strings),str(),colnames(),mean(),median(),range(),sd(),IQR(),summary()
Solution
# dartpoints <- read.csv2(here::here("dartpoints2.csv"), na.strings = "-")
colnames(dartpoints) [1] "Name" "Catalog" "TARL" "Quad" "Length" "Width"
[7] "Thickness" "B.Width" "J.Width" "H.Length" "Weight" "Blade.Sh"
[13] "Base.Sh" "Should.Sh" "Should.Or" "Haft.Sh" "Haft.Or" dartpoints$Weight [1] 3.6 4.5 3.6 4.0 2.3 3.0 3.9 6.2 5.1 2.8 2.5 4.8 3.2 3.8 4.5
[16] 4.4 2.5 2.3 4.2 3.3 3.6 7.4 5.6 4.8 7.8 9.2 6.2 4.3 4.6 5.4
[31] 5.9 5.1 4.7 7.2 2.5 3.9 4.1 7.2 10.7 12.5 13.4 11.1 7.2 28.8 13.9
[46] 9.4 5.3 7.9 7.3 12.2 9.3 11.1 14.8 10.7 11.1 12.3 13.1 6.1 9.2 9.4
[61] 6.7 15.3 15.1 4.6 4.3 11.6 10.5 6.8 9.1 9.4 9.5 10.4 7.5 8.7 6.9
[76] 15.0 11.4 6.3 7.5 5.9 5.4 9.5 5.4 7.1 9.7 12.6 10.5 5.6 4.9 5.2
[91] 16.3mean(dartpoints$Weight)[1] 7.642857median(dartpoints$Weight)[1] 6.8max(dartpoints$Weight) - min(dartpoints$Weight) # or range(dartpoints$Weight)[1] 26.5sd(dartpoints$Weight)[1] 4.207088IQR(dartpoints$Weight)[1] 5.5summary(dartpoints$Weight) Min. 1st Qu. Median Mean 3rd Qu. Max.
2.300 4.550 6.800 7.643 10.050 28.800 Brainstorming
- Why do we visualize data?
- What elements does a good graph contain?
- How are these elements called?
Plots for one variable
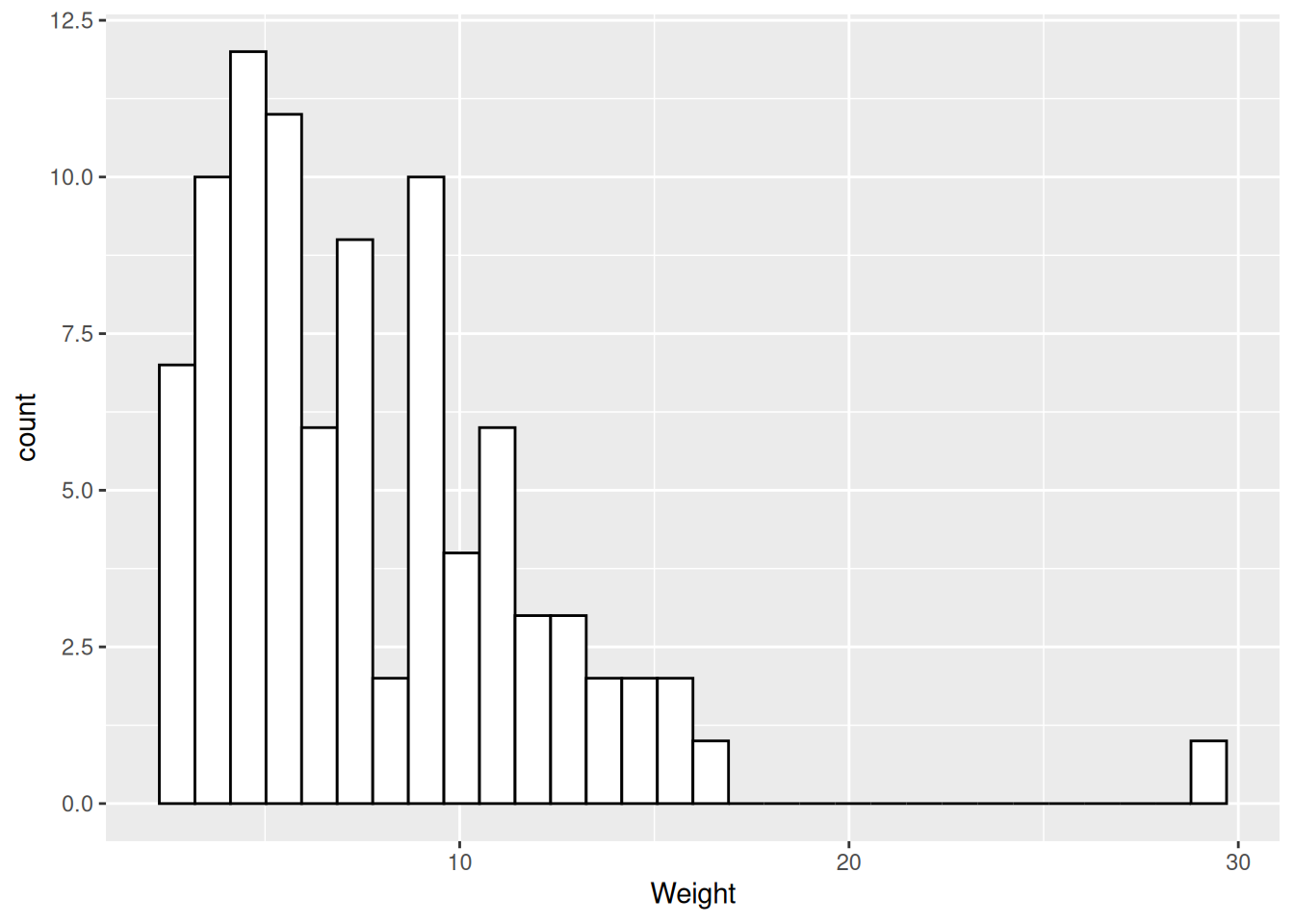
Histogram
- Distribution of values of a quantitative variable.
Distribution of dart point weights.
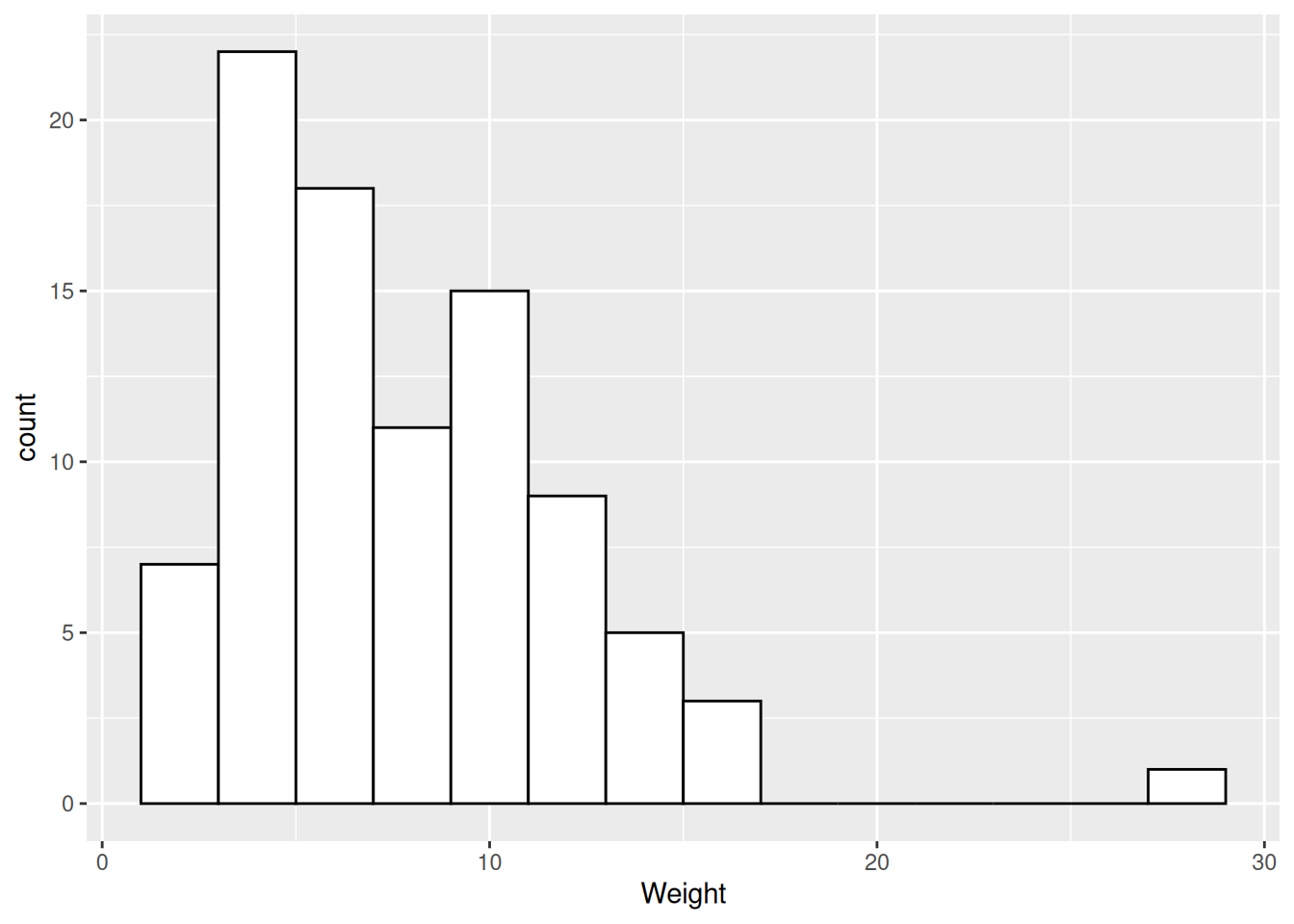
Histogram
- Distribution of values of a quantitative variable.
Distribution of dart point weights, one column (bin) equals 2 g.
Density plot
- Distribution of values of a quantitative variable.
Distribution of dart point weights.
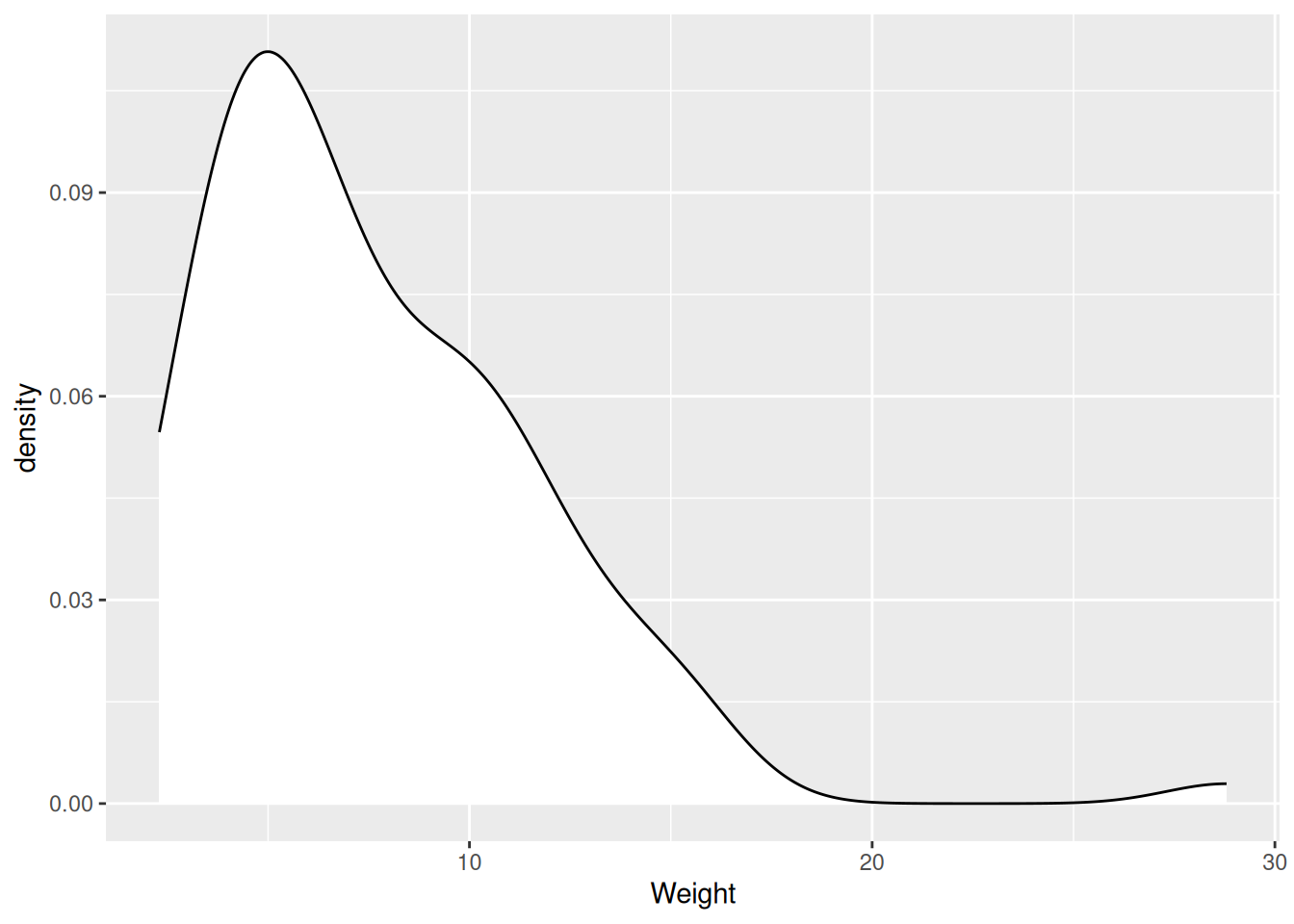
Density plot
- Distribution of values of a quantitative variable, great for comparisons.
Distribution of different types of dart points by weight.
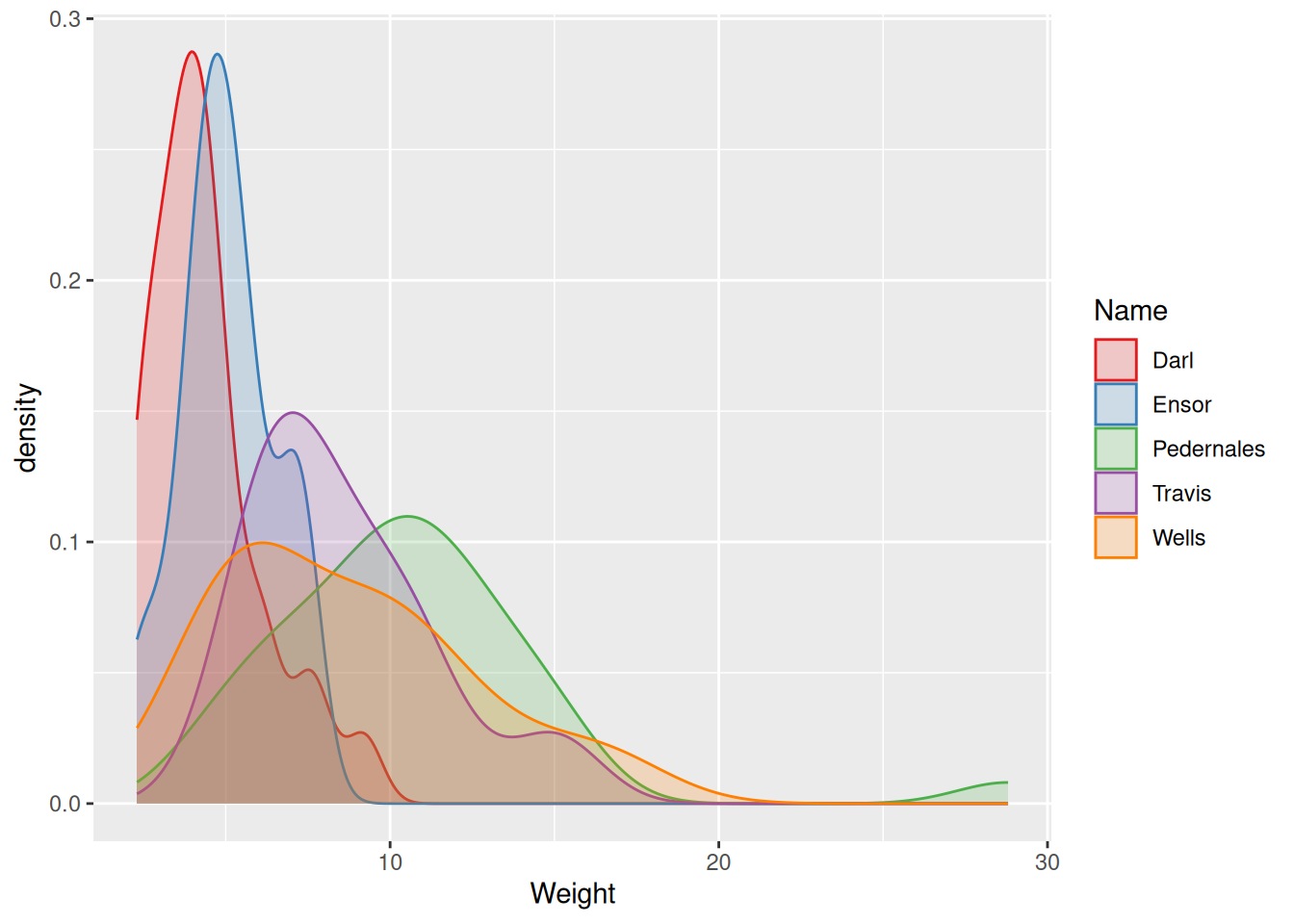
Bar chart
- Distribution of values of a qualitative variable.
Distribution of types of dart points.
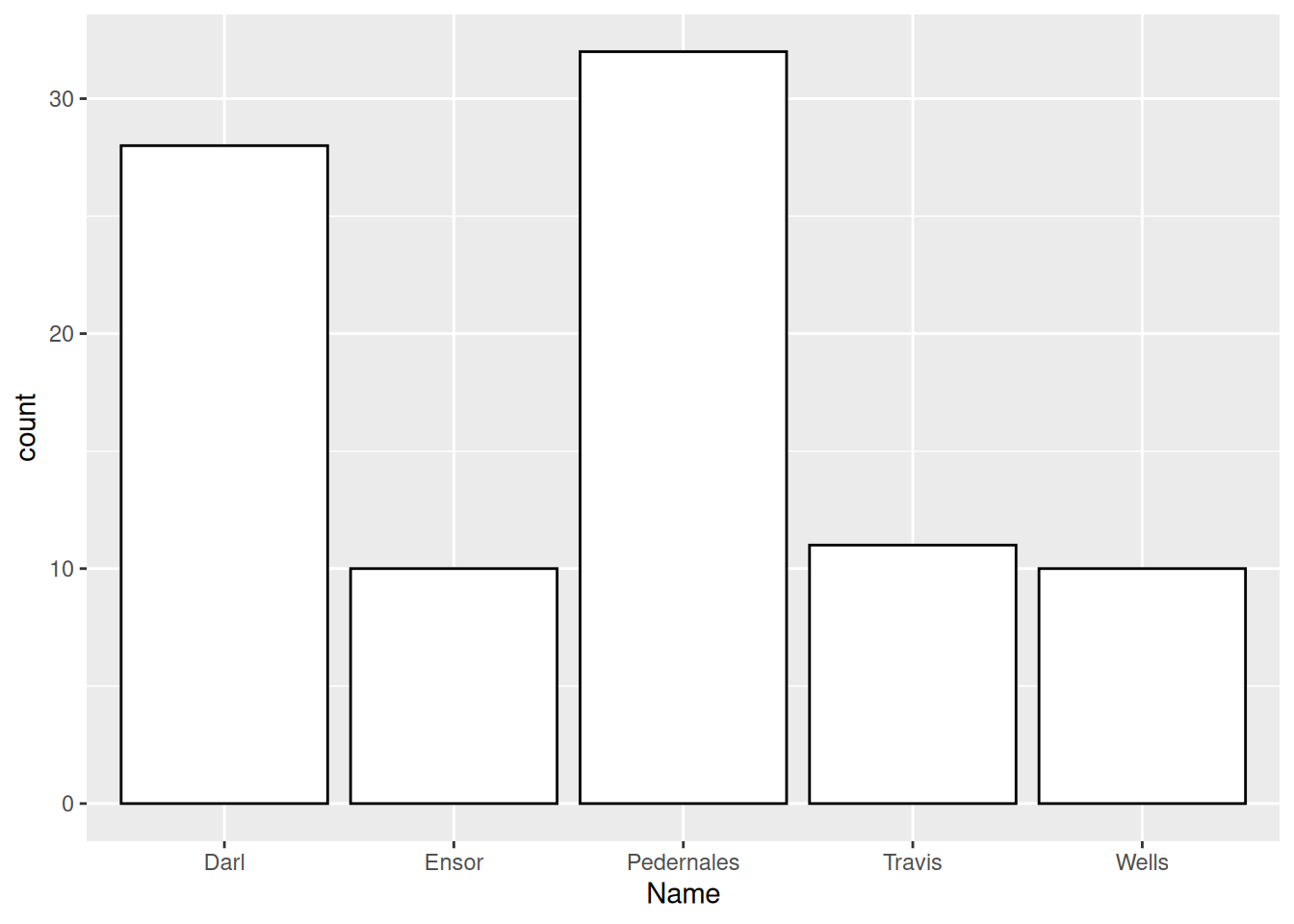
Plots in ggplot2 package
1install.packages("ggplot2")
2library(ggplot2)
3ggplot(data = <your data frame>) +
4 aes(x = <variable to be mapped to axis x>) +
5 geom_<geometry>()- 1
-
Install the package
ggplot2, do this only once.
- 2
-
Load the package from the library of installed packages, do this for every new script.
(Calls tolibrary()function are usually written at the top of the script.)
- 3
-
Function
ggplot()takes the data frame as an argument.
- 4
-
Function
aes()serves to map aesthetics (axis x and y, colors etc.) to different variables from your data frame.
- 5
-
Functons with
geom_prefix are geometries, ie. types of plots to draw.
Geoms for one variable:
geom_histogram()geom_density()geom_bar()
Layers of ggplot2
ggplot(data = dartpoints)
Layers of ggplot2
ggplot(data = dartpoints) +
aes(x = Name)
Layers of ggplot2
ggplot(data = dartpoints) +
aes(x = Name) +
geom_bar()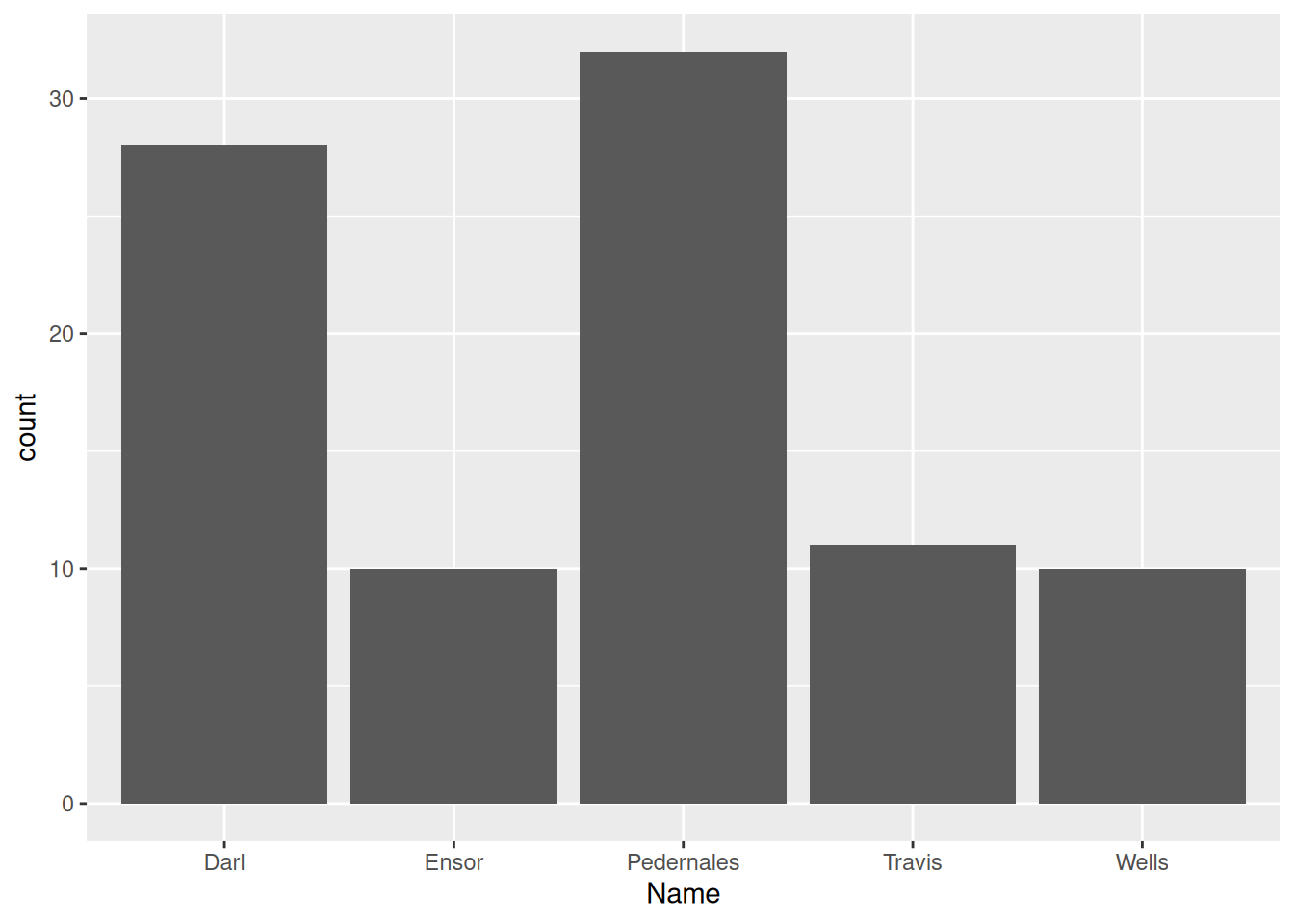
Bar chart
ggplot(data = dartpoints) +
aes(x = Name) +
geom_bar()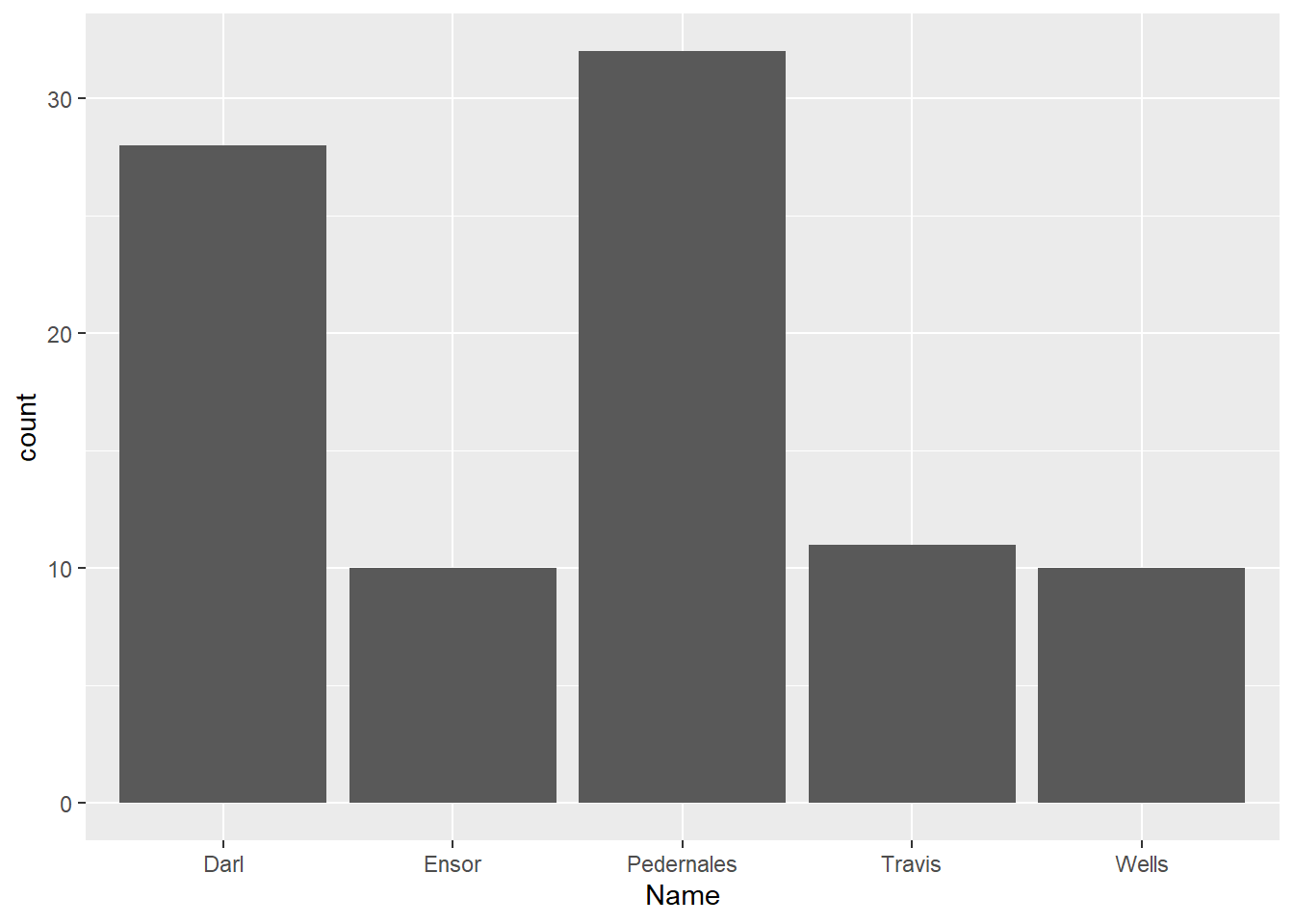
Bar chart
ggplot(data = dartpoints) +
aes(x = Name, color = Name) +
geom_bar()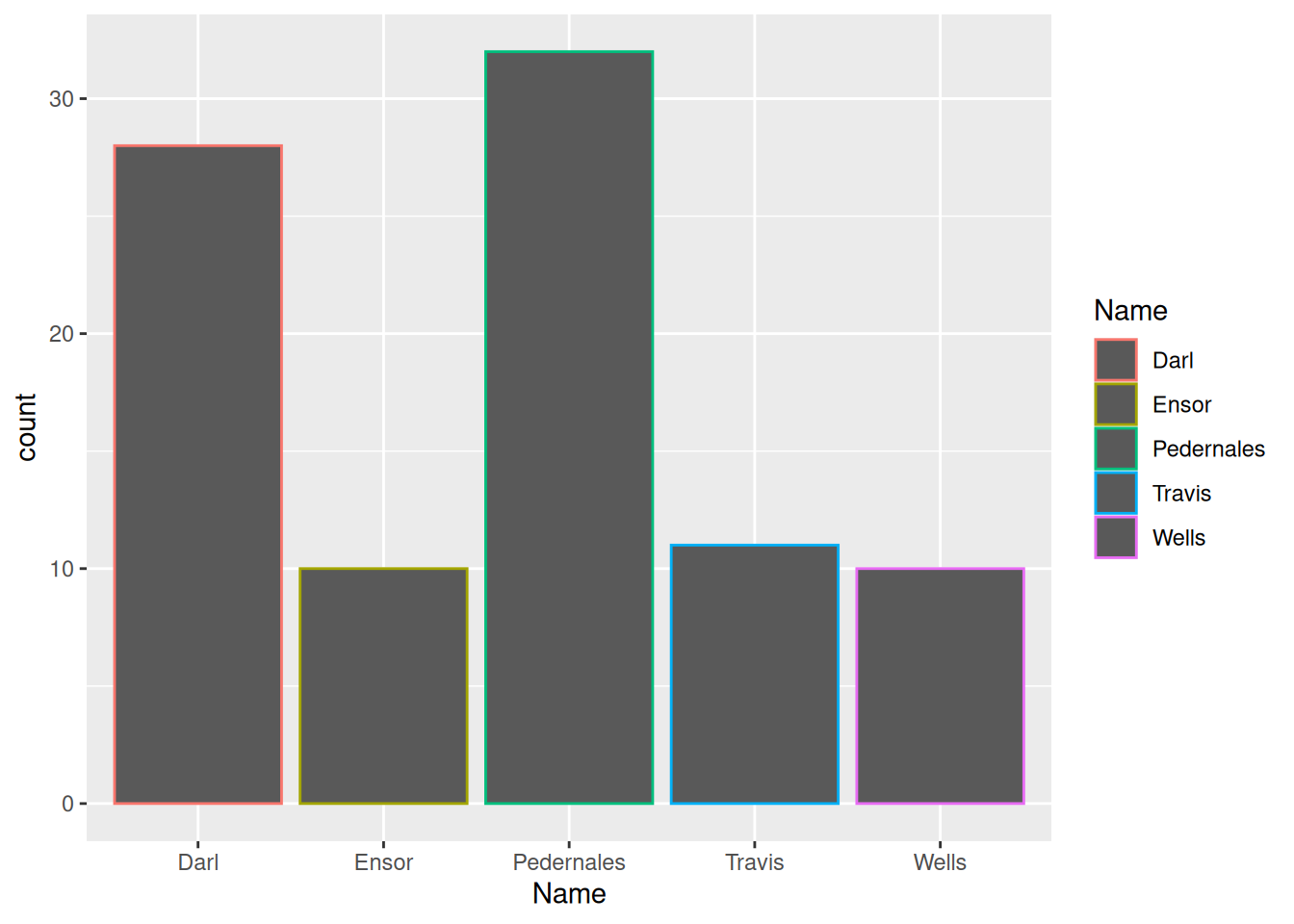
Bar chart
ggplot(data = dartpoints) +
aes(x = Name, color = Name, fill = Name) +
geom_bar()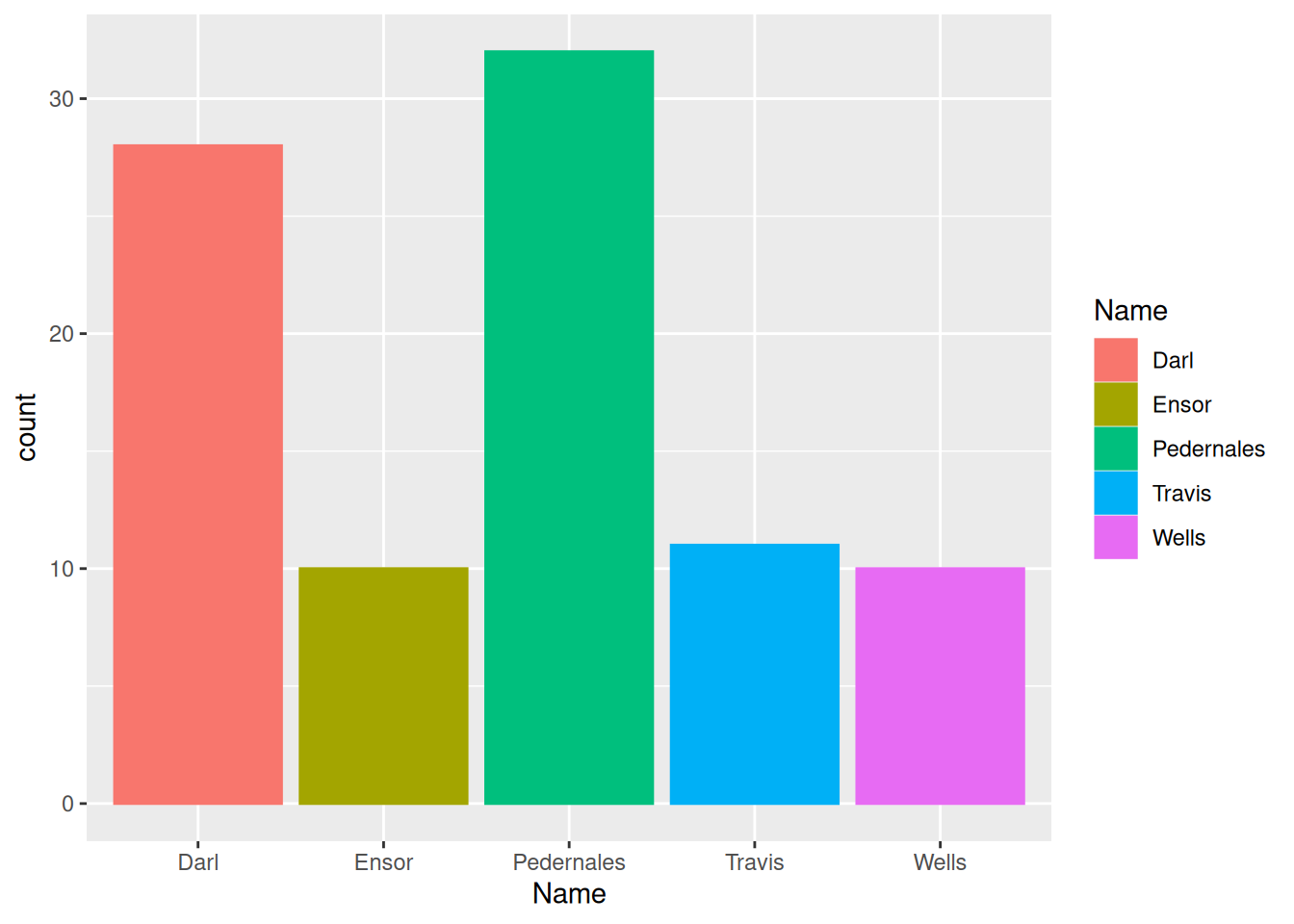
Bar chart
ggplot(data = dartpoints) +
aes(x = Name, fill = Name) +
geom_bar(color = "black")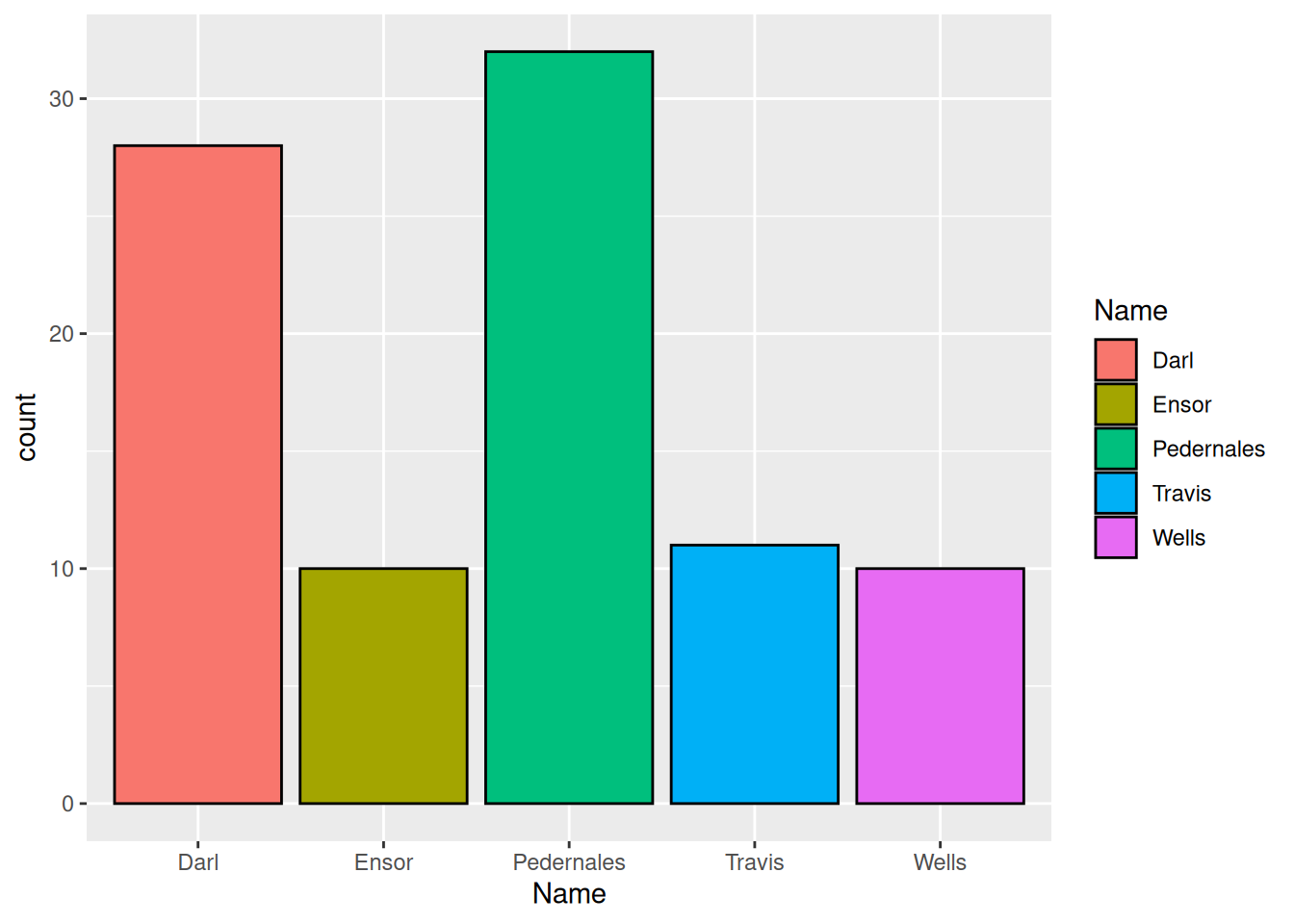
Histogram
ggplot(dartpoints) +
aes(x = Length) +
geom_histogram()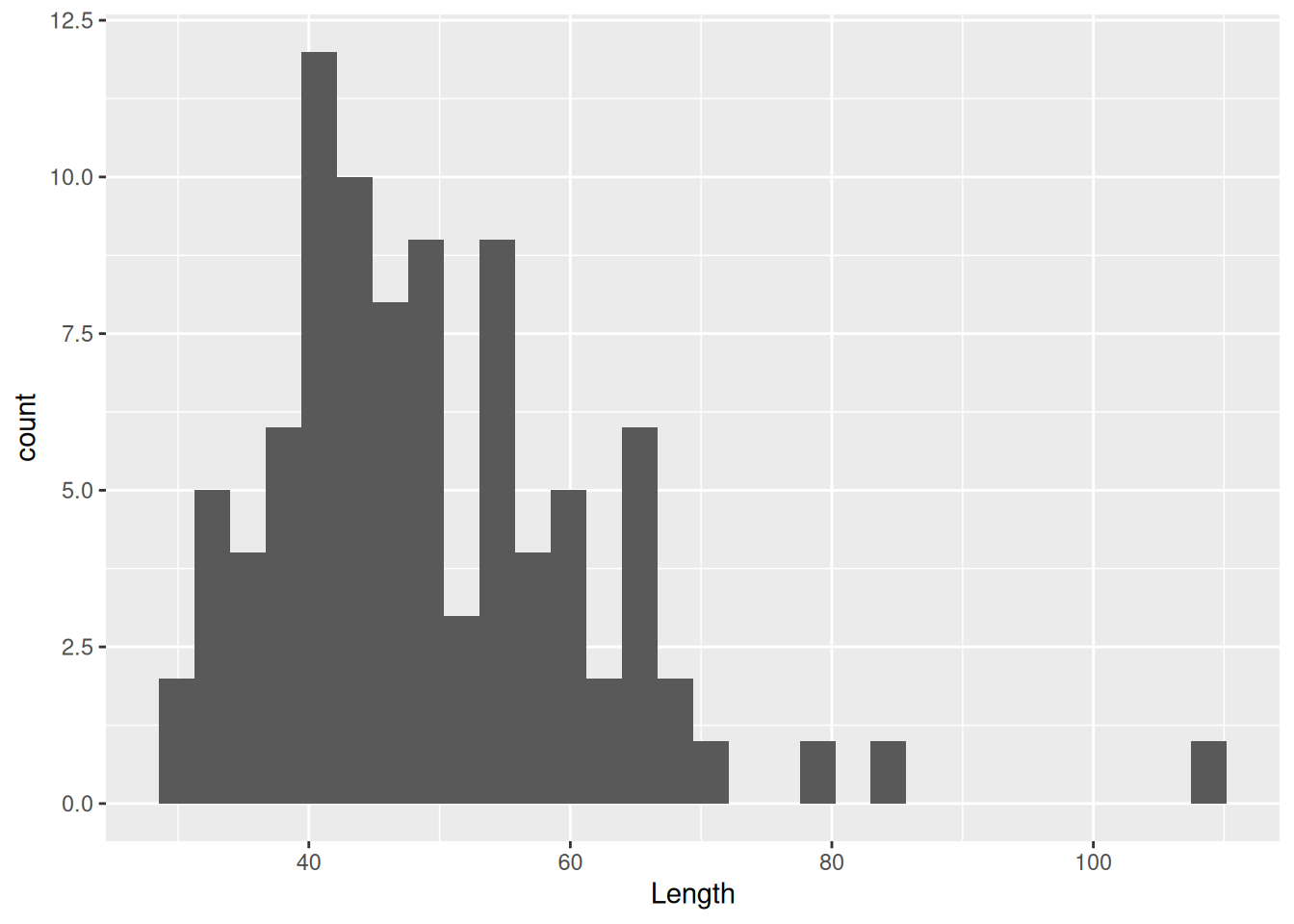
Histogram
ggplot(dartpoints) +
aes(x = Length) +
geom_histogram(binwidth = 5)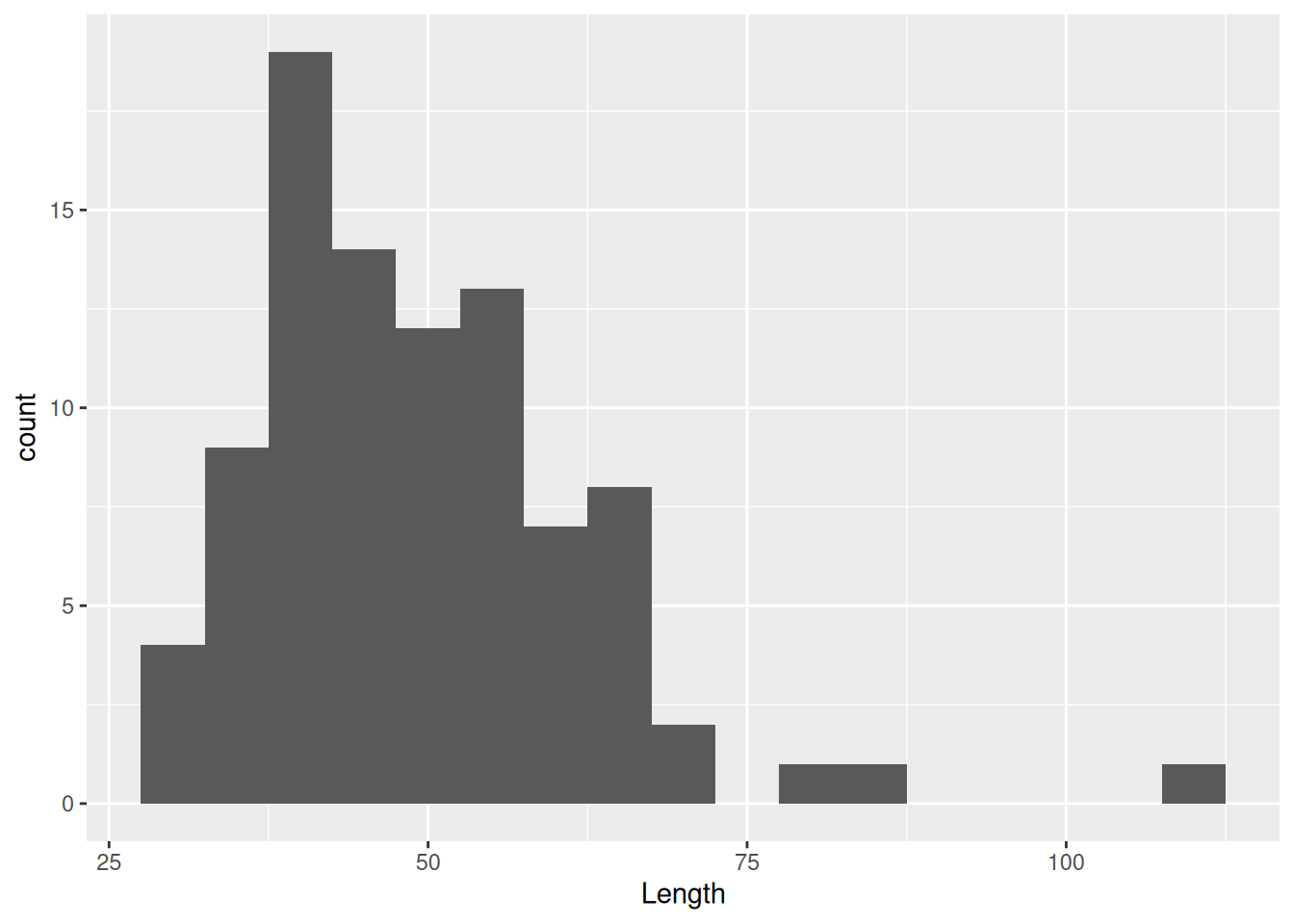
Histogram
ggplot(dartpoints) +
aes(x = Length) +
geom_histogram(binwidth = 5, color = "black")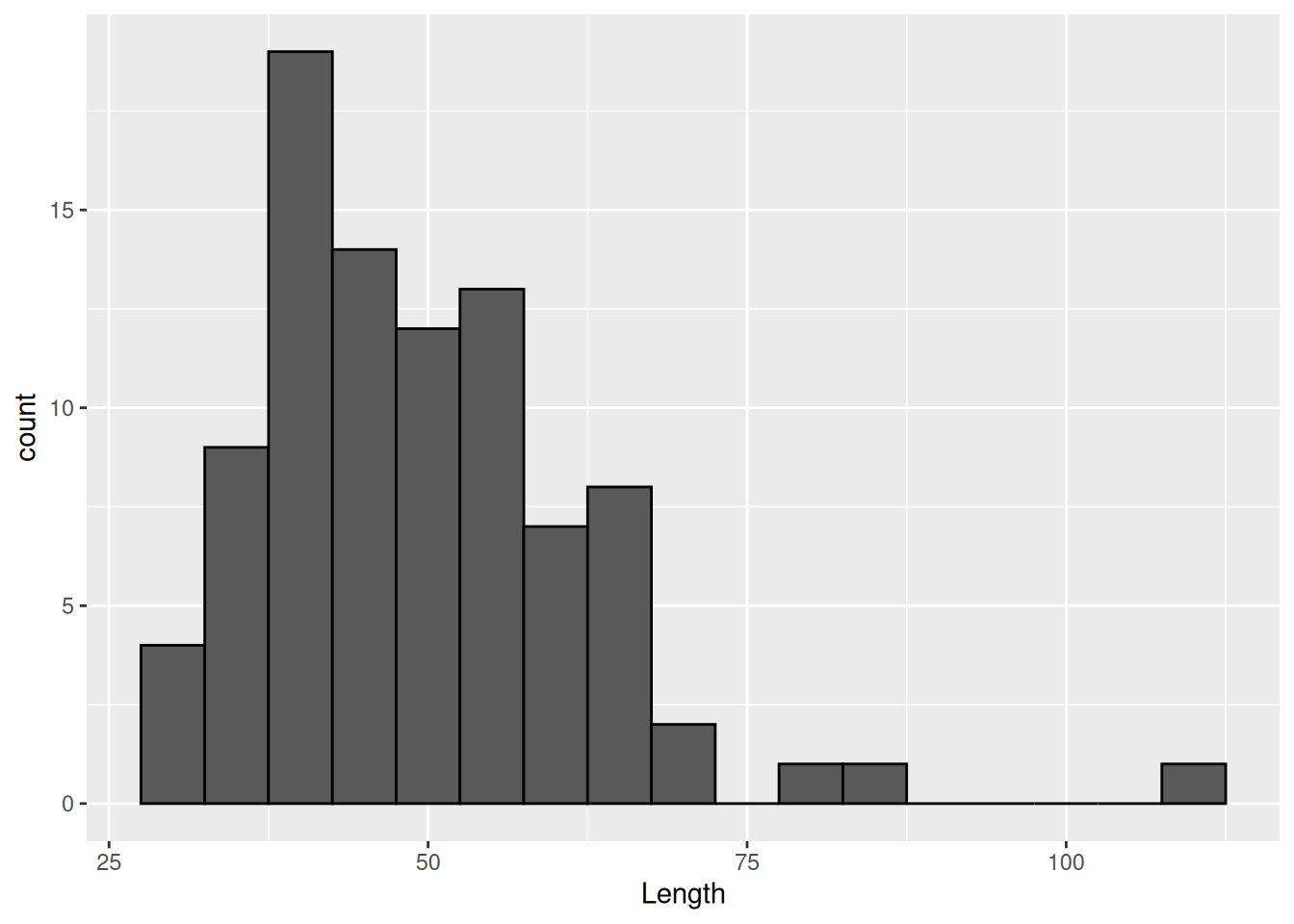
Histogram
ggplot(dartpoints) +
aes(x = Length) +
geom_histogram(binwidth = 5, color = "black", fill = "white")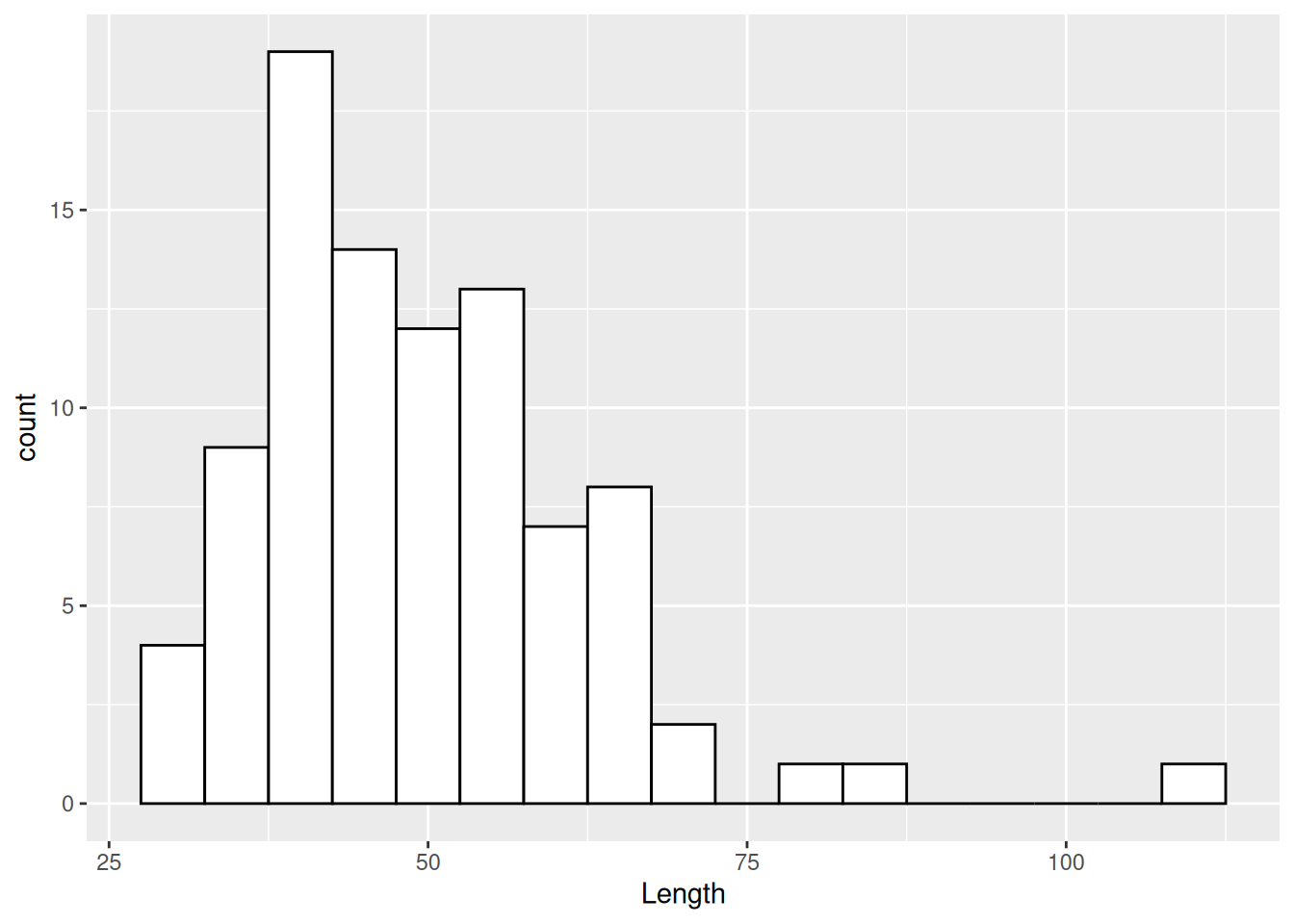
Density plot
ggplot(dartpoints) +
aes(x = Length) +
geom_density()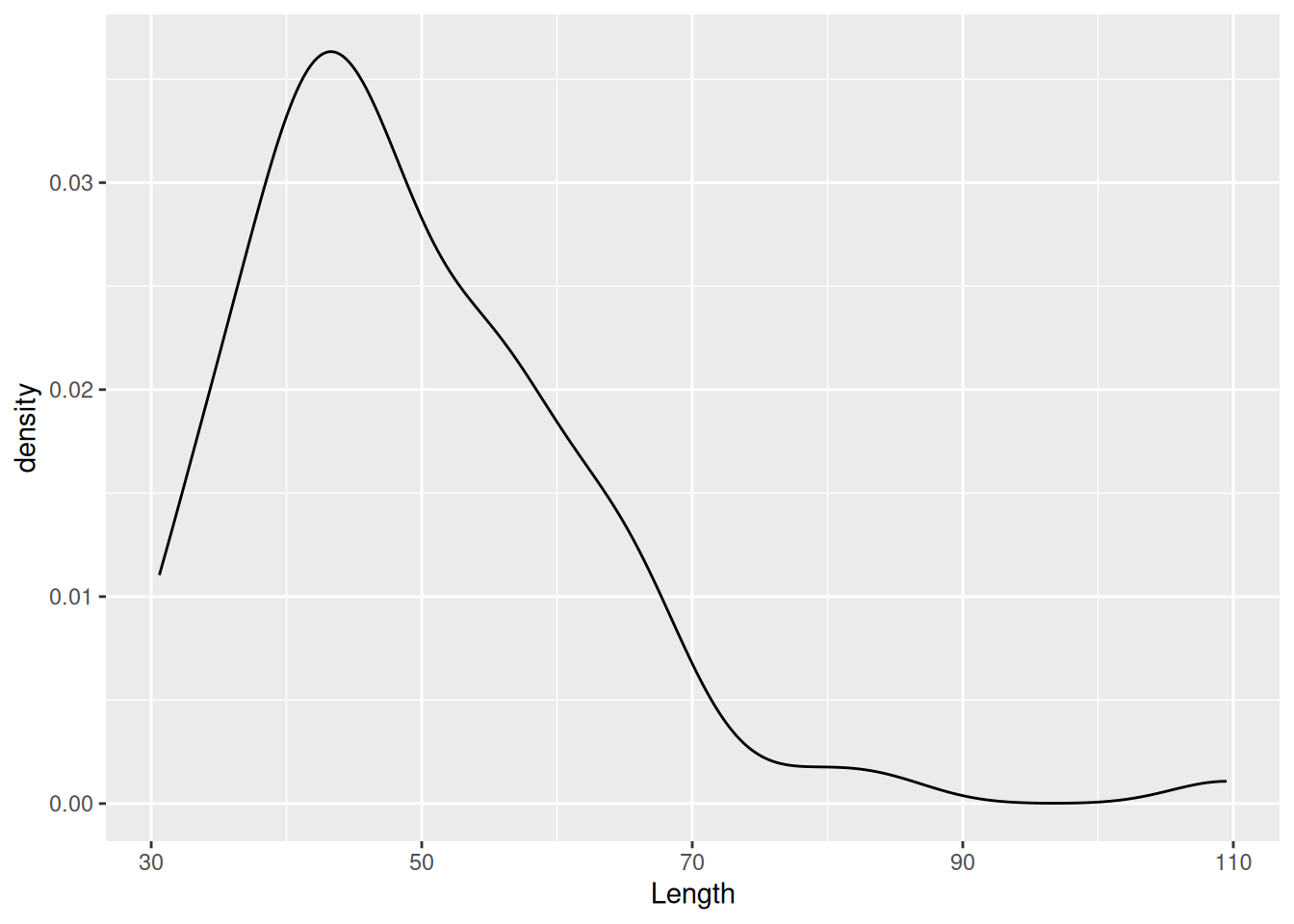
Density plot
ggplot(dartpoints) +
aes(x = Length, color = Name) +
geom_density()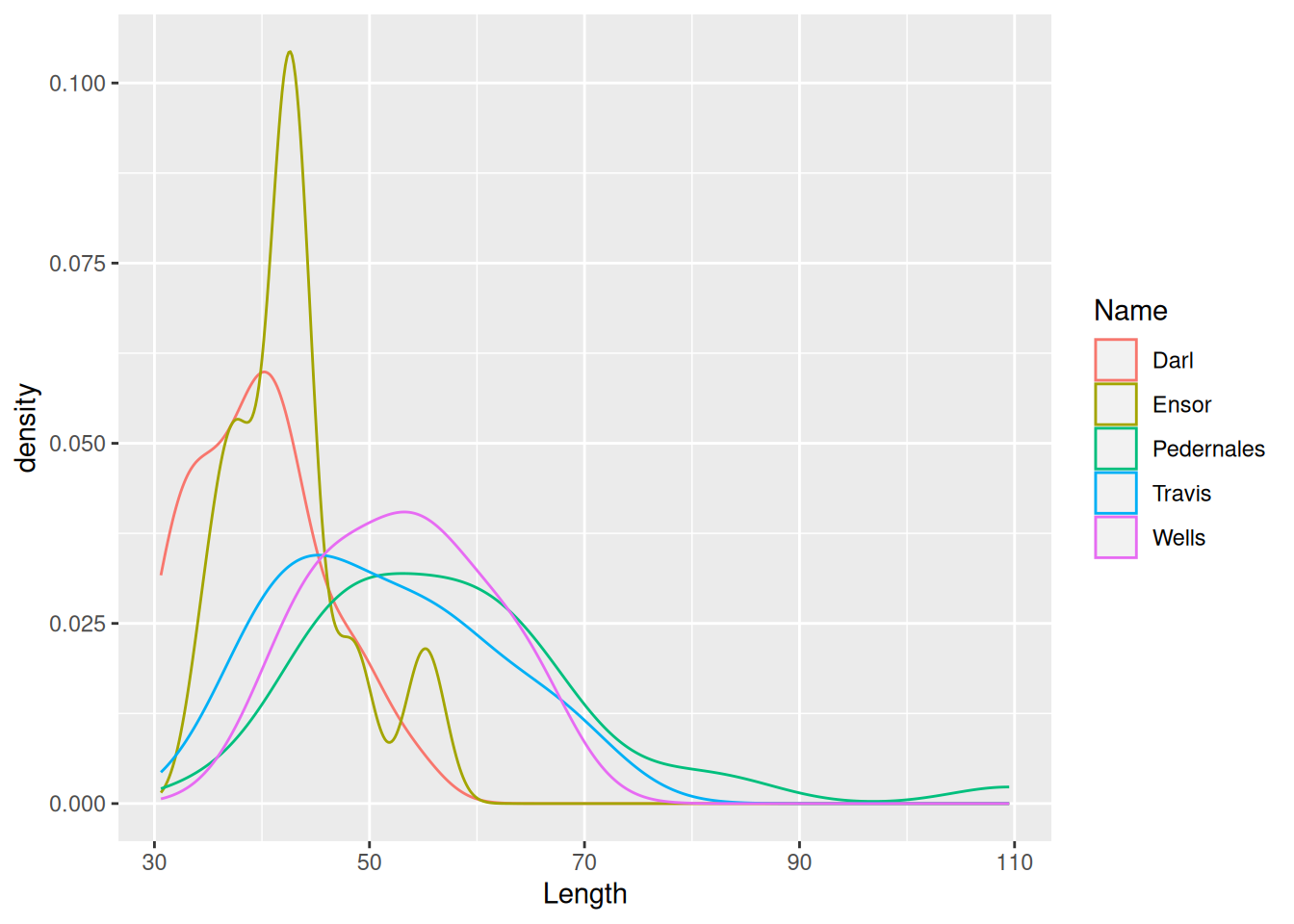
Density plot
ggplot(dartpoints) +
aes(x = Length, color = Name, fill = Name) +
geom_density()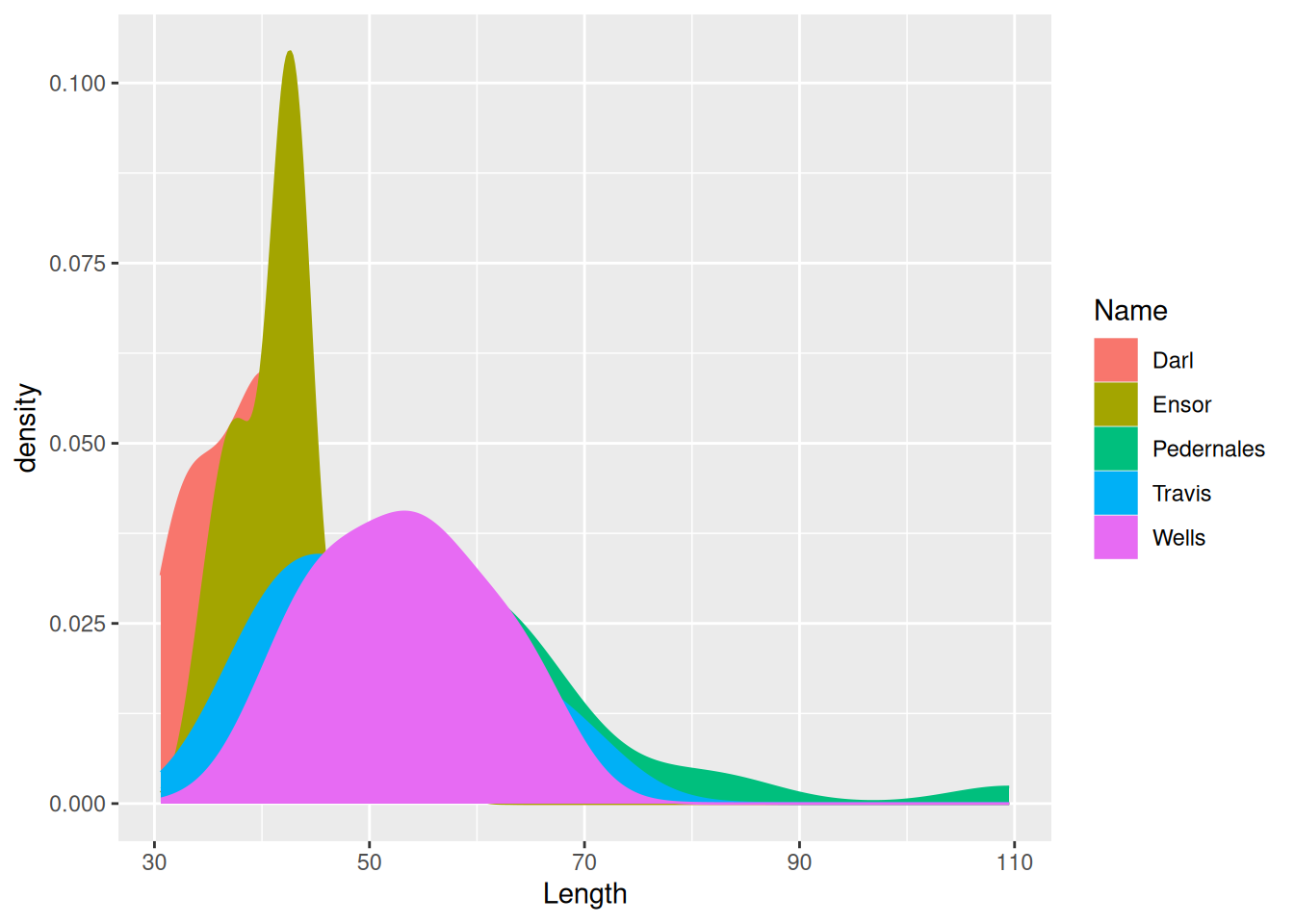
Density plot
ggplot(dartpoints) +
aes(x = Length, color = Name, fill = Name) +
geom_density(alpha = 0.4)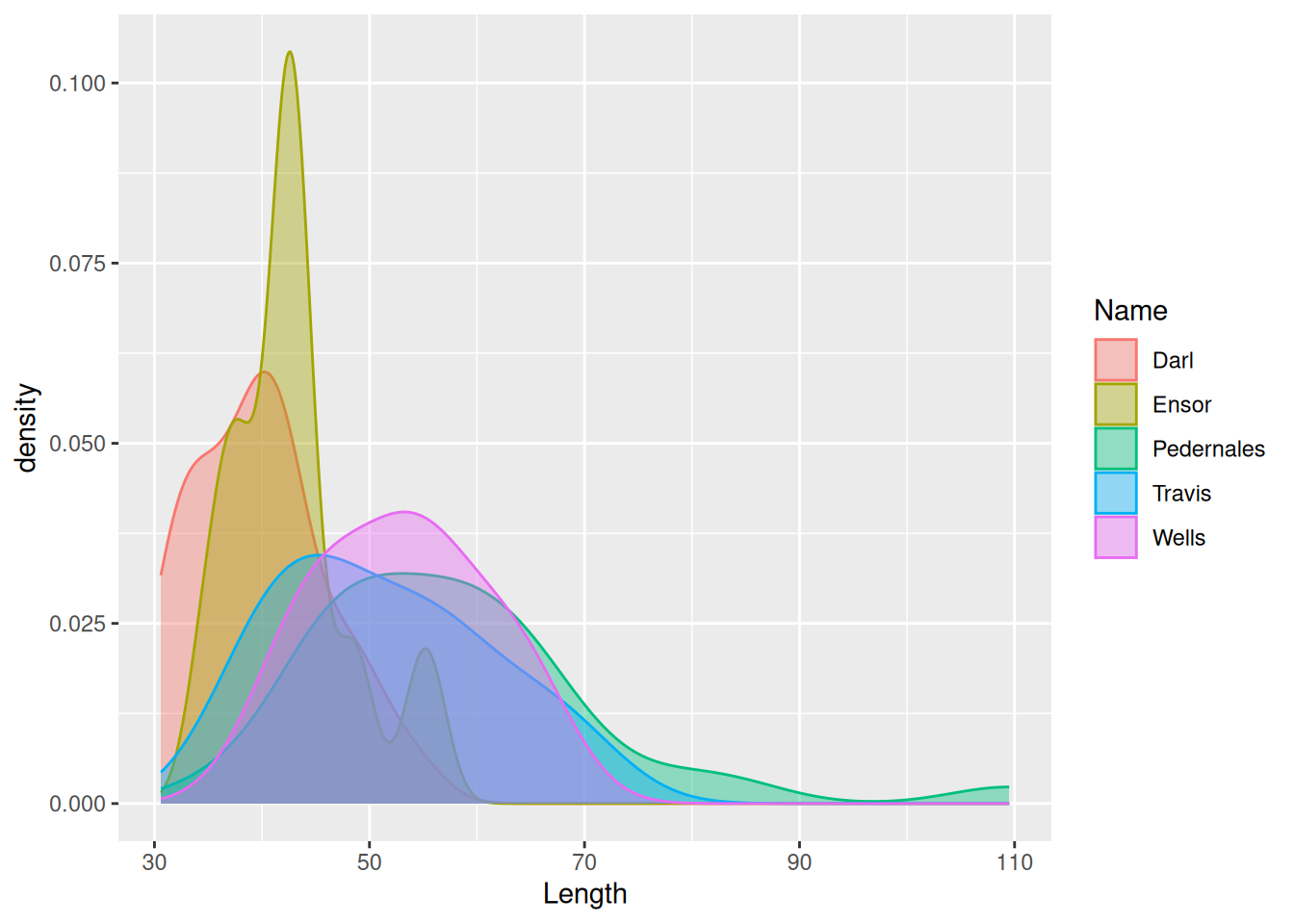
Labels
ggplot(dartpoints) +
aes(x = Length) +
geom_histogram(binwidth = 5, color = "black", fill = "white")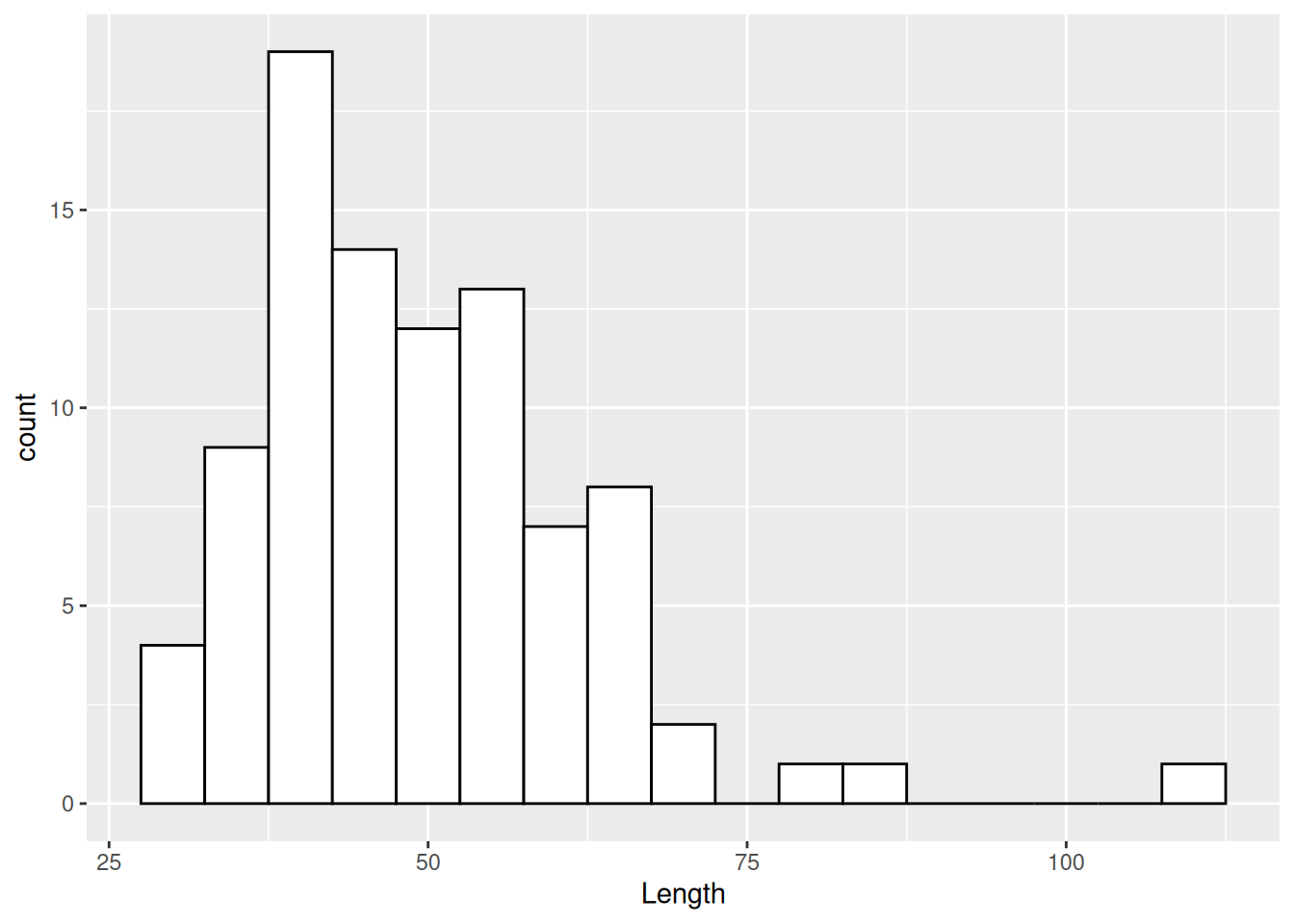
Labels
ggplot(dartpoints) +
aes(x = Length) +
geom_histogram(binwidth = 5, color = "black", fill = "white") +
labs(x = "Length (cm)", y = "Count")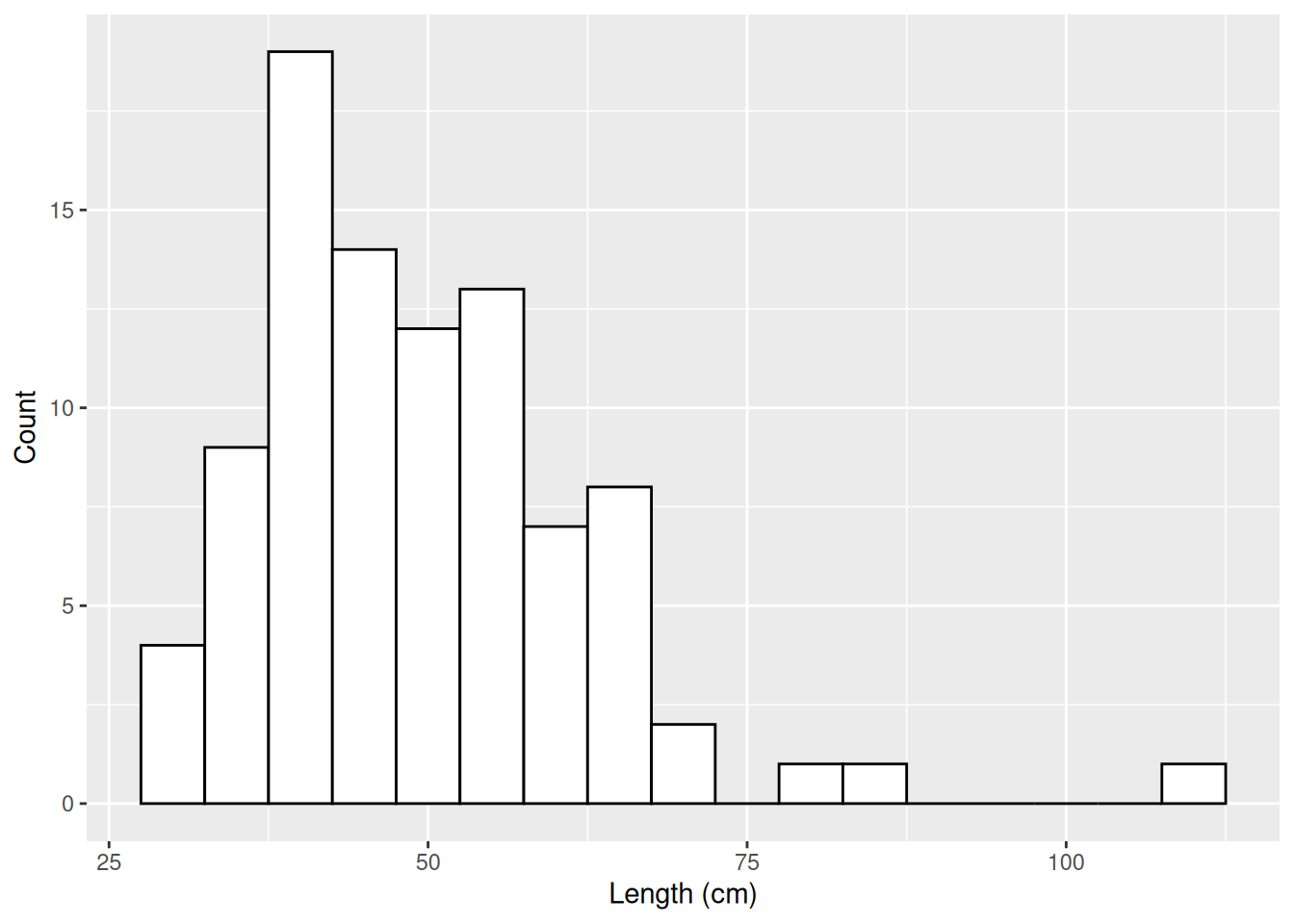
Labels
ggplot(dartpoints) +
aes(x = Length) +
geom_histogram(binwidth = 5, color = "black", fill = "white") +
labs(x = "Length (cm)", y = "Count",
title = "Histogram of dart point lengths")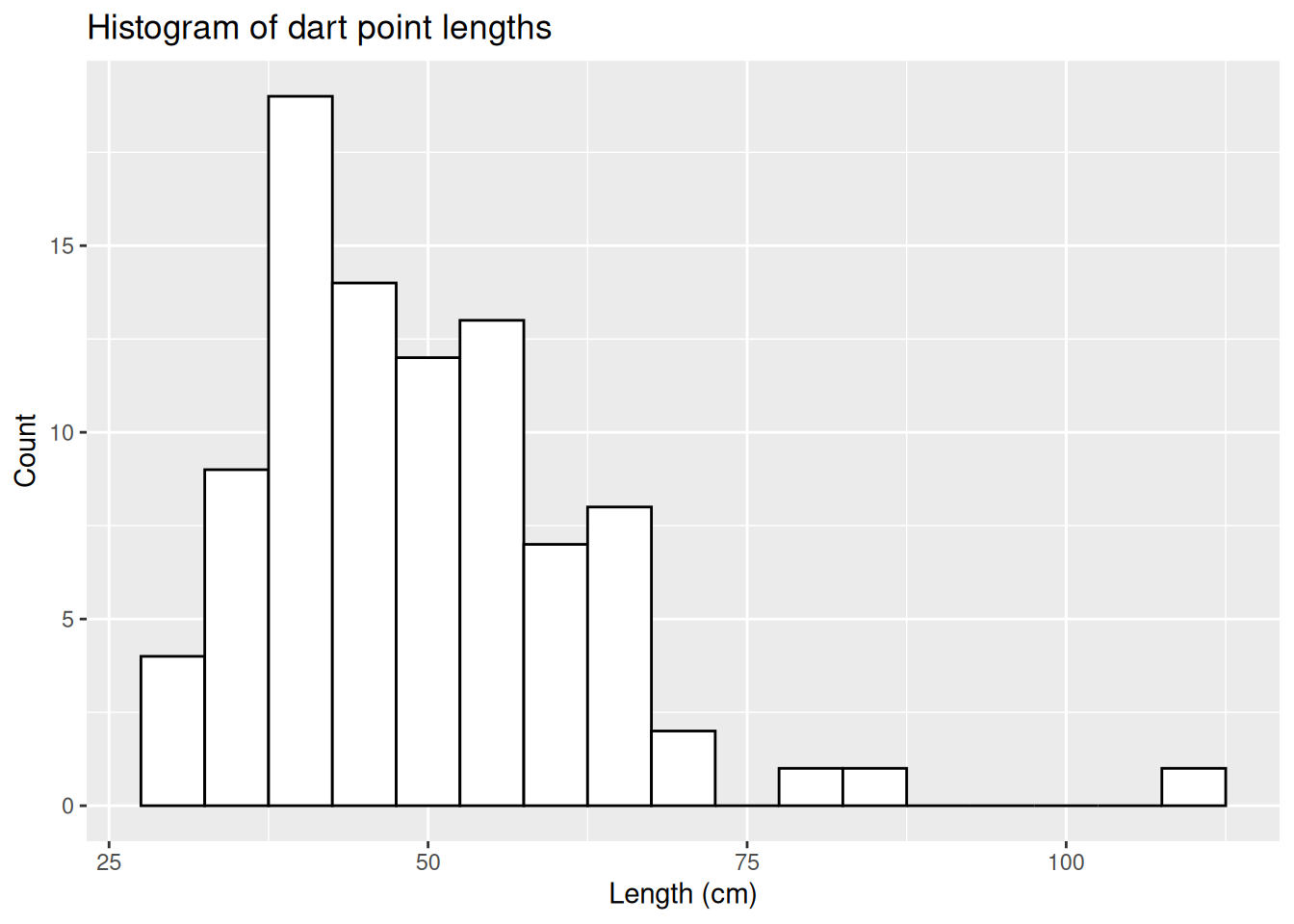
Labels
ggplot(dartpoints) +
aes(x = Length) +
geom_histogram(binwidth = 5, color = "black", fill = "white") +
labs(x = "Length (cm)", y = "Count",
title = "Histogram of dart point lengths",
caption = "Data adapted from archdata R package, Carlson 2017")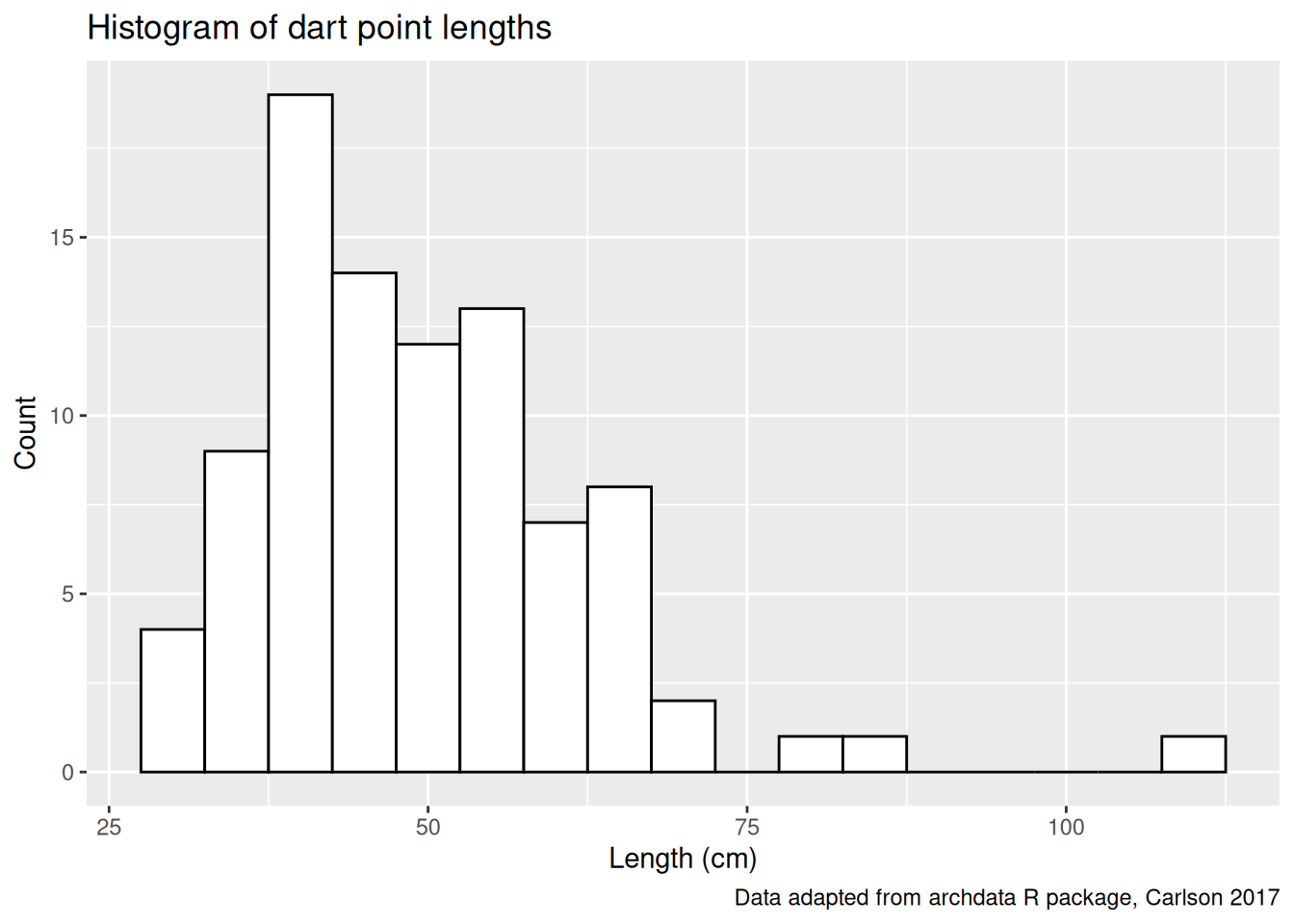
Exercises
Assignments
- Read Make a plot chapter in Data Visualization book by K. J. Healy.
Optional
- Go through Visualize data tutorials here.