grave_number dating sex artefact_type artefact_count artefact_material
1 900 en.zvo male beaker 3 ceramics
2 901 en.zvo female beaker 1 ceramics
3 902 en.zvo male beaker 1 ceramics
4 903 en.zvo female beaker 1 ceramics
5 904 en.zvo male beaker 1 ceramics
6 905 en.zvo female beaker 1 ceramicsDistances and similarity
Distances and similarity
- Distance and similarity are more or less opposite concepts.
- Distance is a numerical measure describing how are two objects (defined by certain variables) different (pairwise distance).
- Different distance measures exist for different data types.
Distance
- Scale 0 – \(\infty\)
- 0 – Two objects with 0 distance between them.
- \(\infty\) – Two objects with infinite distance.
- In practice, maximum distance is often 1.
- Denoted by \(D\) (for distance, or dissimilarity).
- \(D = 1 - S\)
Similarity
- Scale 0 – 1
- 0 – Two objects completely dissimilar (0%).
- 1 – Two objects competely similar (100%).
- Denoted by \(S\) (for similarity).
- \(S = 1 - D\)
Different distance measures
- Dichotomous variables
- Symmetrical – Simple matching distance
- Asymmetrical – Jaccard index (binary distance)
- Categorical variables
- Hamming distance
- Numeric continuous variables
- Euclidean distance
- Mahalanobis distance
- Mixed data sets
- Gower’s distance
Binary distances
- For
TRUE/FALSE,1/0,presence/absence(etc.) data
Symmetrical
- Two presences as match.
- Two absences as match.
If a trait is present, two objects are more similar. If a trait is absent, two objects are more similar. For example if biological sex is encoded in one variable with 0 for male and 1 for female, it is symmetrical.
- Simple maching distance
Asymmetrical
- Two presences as match.
- Two absences as mismatch.
If a trait is present, two objects are more similar. If a trait is absent in both cases, e.g. undetermined, missing etc., this does not affect similarity. This is more practical in archaeology.
- Jaccard index, i.e. binary distance
dist(x, method = "binary")
Distance between (continuous) numeric data
- To remove effects of scale (different units etc.), variables should be scaled (normalized).
Normalization
- z-score or z-transformation
\[ z = \frac{x - \mu}{\sigma} \]
Euclidean distance
- Defined for a Cartesian coordinate space.
- Uses Pythagorean theorem.
\[ d(p, q) = \sqrt{(q_1 - p_1)^2 + (q_2 - p_2)^2} \]
In R…
Normalization:
scale(x, center = TRUE, scale = TRUE)
Euclidean distance:
dist(x, method = "euclidean")
Example – Binary distance
Exercise with the Eneolithic/BA burial ground ( burials.csv).
# artefact counts to presence (TRUE/FALSE)
graves <- graves0 |>
mutate(artefact_presence = artefact_count >= 1)
head(graves) grave_number dating sex artefact_type artefact_count artefact_material
1 900 en.zvo male beaker 3 ceramics
2 901 en.zvo female beaker 1 ceramics
3 902 en.zvo male beaker 1 ceramics
4 903 en.zvo female beaker 1 ceramics
5 904 en.zvo male beaker 1 ceramics
6 905 en.zvo female beaker 1 ceramics
artefact_presence
1 TRUE
2 TRUE
3 TRUE
4 TRUE
5 TRUE
6 TRUETable transformation
# long table -> wide table
graves_artefacts <- graves |>
tidyr::pivot_wider(
id_cols = c("grave_number"),
names_from = "artefact_type",
values_from = "artefact_presence",
values_fill = FALSE # fill in missing values with FALSE
)
head(graves_artefacts)# A tibble: 6 × 13
grave_number beaker dartpoint wristguard dagger axe bowl beam beam_amber
<int> <lgl> <lgl> <lgl> <lgl> <lgl> <lgl> <lgl> <lgl>
1 900 TRUE TRUE TRUE TRUE TRUE TRUE FALSE FALSE
2 901 TRUE TRUE TRUE FALSE FALSE TRUE TRUE FALSE
3 902 TRUE TRUE TRUE FALSE FALSE TRUE FALSE FALSE
4 903 TRUE TRUE TRUE FALSE FALSE TRUE TRUE FALSE
5 904 TRUE TRUE TRUE FALSE FALSE TRUE FALSE FALSE
6 905 TRUE TRUE TRUE FALSE FALSE TRUE TRUE FALSE
# ℹ 4 more variables: koflik <lgl>, bracelet_bronze <lgl>, needle <lgl>,
# spear <lgl>Count distance
# matrix with logical variables only
artefacts <- graves_artefacts |>
select(where(is.logical)) |>
as.matrix()
# add row names to the matrix
rownames(artefacts) <- graves_artefacts$grave_number
artefacts[1:6, 1:6] beaker dartpoint wristguard dagger axe bowl
900 TRUE TRUE TRUE TRUE TRUE TRUE
901 TRUE TRUE TRUE FALSE FALSE TRUE
902 TRUE TRUE TRUE FALSE FALSE TRUE
903 TRUE TRUE TRUE FALSE FALSE TRUE
904 TRUE TRUE TRUE FALSE FALSE TRUE
905 TRUE TRUE TRUE FALSE FALSE TRUE# count Jaccard (binary) distance
d <- dist(artefacts, method = "binary", diag = TRUE)
as.matrix(d)[1:6, 1:6] 900 901 902 903 904 905
900 0.0000000 0.5000000 0.3333333 0.4285714 0.3333333 0.4285714
901 0.5000000 0.0000000 0.3333333 0.1666667 0.3333333 0.1666667
902 0.3333333 0.3333333 0.0000000 0.2000000 0.0000000 0.2000000
903 0.4285714 0.1666667 0.2000000 0.0000000 0.2000000 0.0000000
904 0.3333333 0.3333333 0.0000000 0.2000000 0.0000000 0.2000000
905 0.4285714 0.1666667 0.2000000 0.0000000 0.2000000 0.0000000- Result is a distance matrix.
- It is symmetrical. Lower triangular is the same as upper triangular.
- On the diagonal, there is distance of the given object to itself, i.e. 0.
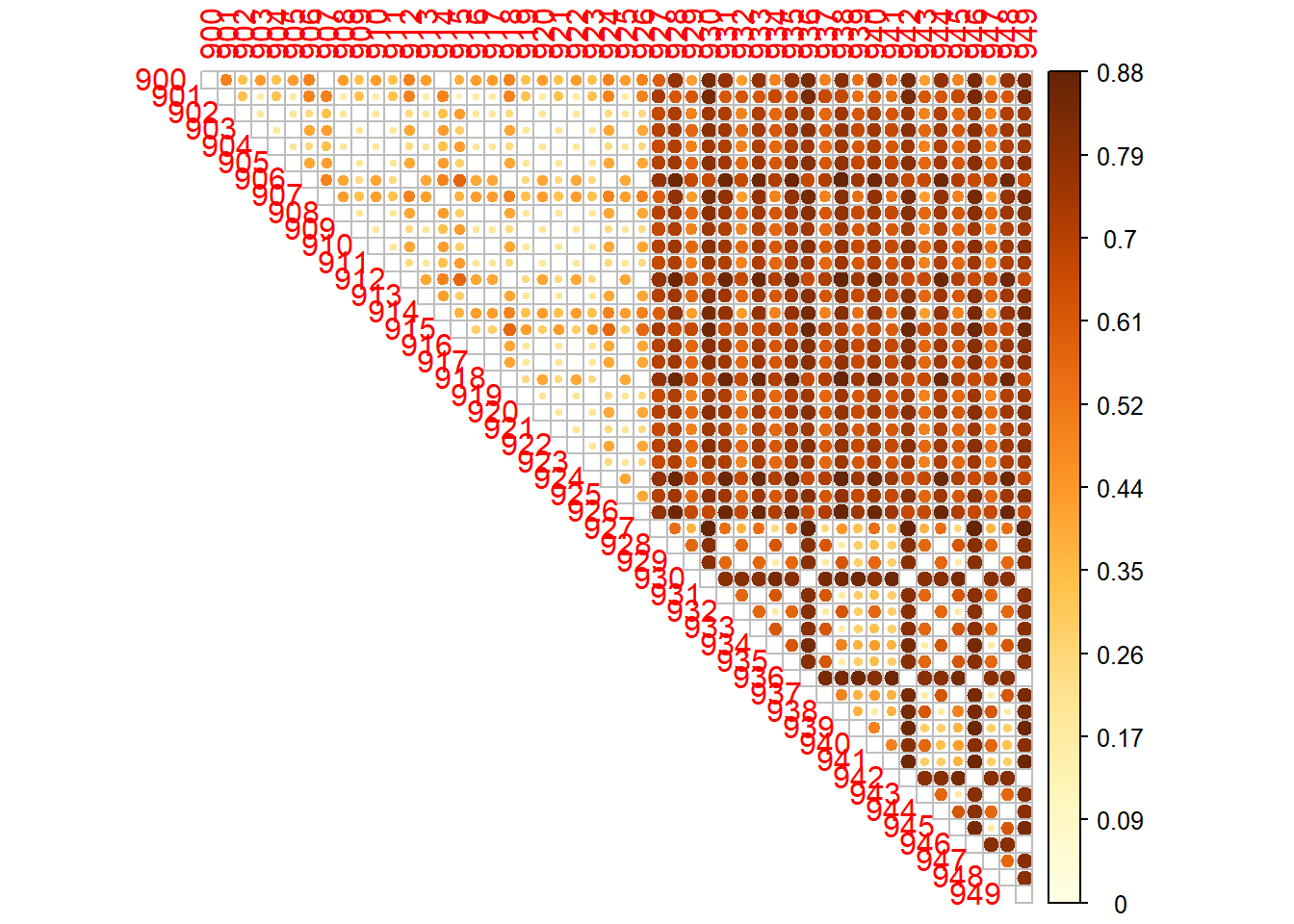
Visualizing distance matrix
- Package
corrplothas a nice way of plotting heat maps.
Resources
For a much more detailed overview of distance methods, see the tutorial on classification by Schmidt, S. C. et al. DOI: 10.5281/zenodo.6325372 (direct link to a HTML file is here).
AES_707 Statistics seminar for archaeologists | Disctances